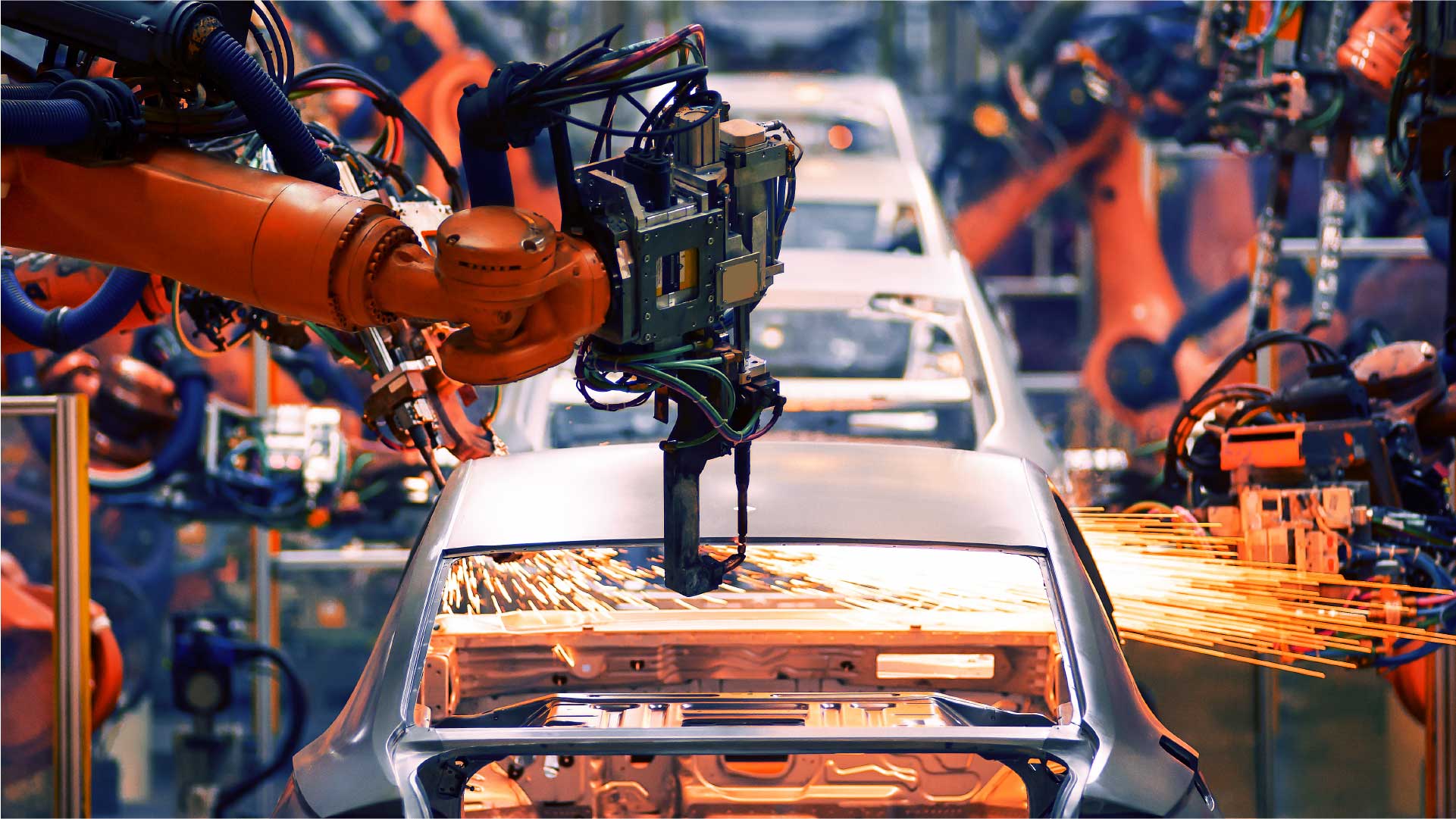
Imagine a world where machines can move with extreme precision and power, carrying out previously unthinkable jobs. Linear actuators, adaptable tools that transform electrical energy into linear mechanical motion, are at the center of this technology change. Linear actuators are transforming businesses around the world, from factory automation to consumer gadgets.
As the name suggests, linear actuators are machines that turn electrical energy into a motion that moves in a straight line. They have a motor, a clutch, and either a screw mechanism or a rack and pinion mechanism. This simple but powerful design has been a key part of handling many tasks and making businesses more efficient across many fields for linear actuators.
Applications of Linear Actuators
Because of their versatility and adaptability, linear actuators have found applications in many different fields:
Industrial Automation
In the business world, straight-line actuators are used to automate hard, repeated tasks:
- Robotic systems. In this field, motors provide the necessary linear motion for robotic arms, enabling them to perform tasks with precision and speed.
- Conveyor systems. These mechanisms let you change the heights, angles, and speeds of conveyor systems. They make sure that moving materials around in factories is smooth and quick.
Automotive Industry
The following list of applications shows how linear actuators are transforming the automotive industry:
- Electric vehicles. For the steering, suspension, and HVAC systems in electric cars, straight-line motors are crucial for controlling a variety of parts. They work precisely and quickly, which improves the total performance and ease of electric cars.
- Adjustable seating and mirrors. Linear actuators let drivers change the positions of their seats and mirrors to get the best vision and comfort. This function makes driving safer and less tiring.
Aerospace and Defense
In the aerospace and defense industries, linear actuators find use in a variety of applications.
- Control surfaces. Linear actuators are very important for controlling the ailerons, rudders, and elevators on an airplane. In order to ensure safe and maneuverable flight, their reliability and precision are crucial.
- Cargo handling systems. Straight-line actuators are used in cargo handling systems to automate the loading and unloading of equipment and supplies. They provide efficient and precise movements, reducing the risk of human error.
Medical Equipment
In the medical industry, linear motors have also helped by enhancing patient care and reducing the workload of medical staff. Here are some applications:
- Surgical tables. They make it possible to precisely place and change surgical tables, making sure that both patients and doctors are as comfortable and easy to reach as possible.
- Patient lifts. They are used in patient lifts to assist with transferring patients, reducing the physical strain on caregivers.
Consumer Electronics
Even in consumer electronics, linear drivers have found their place:
- Adjustable desks. Adjustable desk heights are made possible by straight-line movers, improving ergonomics and reducing back and neck pain.
- Home automation systems. These mechanisms are integrated into home automation systems to control curtains, blinds, or even doors.
Benefits of Using Linear Actuators
Linear motors have a number of benefits that make them desirable for a variety of applications, including:
- Precision and accuracy.Straight-line drivers are renowned for their exact and precise movements, ensuring dependable performance in applications requiring high levels of control.
- Space efficiency. Their small size makes it simple to integrate them into different systems, which saves room.
- Reduced maintenance costs. They are simple to maintain, reducing downtime and running expenses.
- Customizability. You can change things about them to fit your needs, like the load size, speed, and stroke length.
Choosing the Right Linear Actuator
Understanding the technical specifications of linear actuators is crucial for choosing the right device for specific applications. Here are the most important details to think about:
1. Load Capacity
It is always important to make sure that actuators can do their jobs without any problems. Here are the loads that each type of actuator can handle:
- Electric straight-line movers. Depending on the design and purpose, they can range from 100 N (22 lbs.) to over 10,000 N (2,248 lbs.
- Pneumatic motors. Between 100 N (22 lbs) and 5,000 N (1,124 lbs), they can handle loads. Larger industrial types can handle loads above this range.
- Hydraulic drivers. Heavy-duty applications can use these actuators to handle loads ranging from 1,000 N (224 lbs) to over 50,000 N (11,240 lbs).
- Stepper and servo motors. Depending on how they are set up and what they are used for, their load capacities range from a few hundred grams to several hundred kilograms.
2. Speed Ranges
Depending on how they are set up and what they are used for, their load capacities range from a few hundred grams to several hundred kilograms.
- Electric linear actuators. The typical speed range is 5 mm/s (0.2 in/s) to 100 mm/s (3.9 in/s), with some high-performance types reaching speeds of up to 300 mm/s (11.8 in/s).
- Pneumatic actuators. Depending on the pressure and design, they offer faster speeds that range from 50 mm/s (2 in/s) to over 500 mm/s (19.7 in/s).
- Hydraulic actuators. The system design can make the speed range from 10 mm/s (0.4 in/s) to 200 mm/s (7.9 in/s).
- Stepper and servo motors. They can reach speeds of a few hundred to several thousand RPM, which translates to straight-line speed, depending on the configuration of their gears.
3. Power Requirements
Power requirements tell you how much electricity or gas energy the motor needs to work properly and be compatible with other systems:
- Electric motors. With power ratings ranging from 10 W to over 500 W for heavy-duty applications, they operate on standard voltages (12V, 24V, or 48V DC).
- Pneumatic movers. Need air that is squeezed to a pressure of 3 bar (43 psi) to 8 bar (116 psi). The flow rate and pressure will determine the power consumption.
- Hydraulic drivers. Work at pressures between 70 bar (1,015 psi) and over 350 bar (5,076 psi), and the amount of power needed depends on the flow rate of the hydraulic fluid.
- Stepper and servo motors. While servo motors typically operate within a range of tens to hundreds of watts depending on their purpose, stepper motors can require anywhere from a few watts up to several hundred watts.
Because of their precision, reliability, and versatility, linear actuators are crucial in many fields. You can improve speed, boost productivity, and encourage new ideas by taking advantage of their benefits.